InvestGlass: The Role of ERP in Business Process Optimization

In today’s fast-paced business environment, efficient operations management across the entire organization is essential for success. Digital transformation is a key driver in modernizing these operations. This is where an enterprise resource planning system becomes a game-changer. By integrating critical functions such as inventory management systems, finance, human resources, and more, ERP systems enable businesses to streamline processes and enhance productivity. ERP vendors continually innovate to provide solutions that help organisations reduce costs and optimize workflows. But how exactly does an enterprise resource planning system refine business processes to benefit the organization? InvestGalss offers a full inventory management system hosted in Switzerland or on-premise. Let’s explore this in detail.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a powerful business management software that integrates all aspects of an organization’s operations into a unified system. By providing real-time visibility into the inner workings of a business, ERP systems help automate and streamline back-office tasks, enabling employees to become more productive and successful in their roles. These systems are designed to manage and integrate various business functions, including financial management, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management (CRM). With an ERP system, businesses can ensure that all departments are working with the same data, reducing discrepancies and enhancing overall efficiency.
Benefits of ERP Systems
ERP systems offer a multitude of benefits to organizations, making them an invaluable tool for business process optimization. Some of the key advantages include:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: By automating routine tasks and providing a centralized data repository, ERP systems help streamline operations and reduce manual effort.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: With real-time data and analytics, business leaders can make informed decisions quickly and accurately.
- Reduced Costs: ERP systems help in better financial management, reducing operational costs and improving profitability.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Enhanced customer relationship management capabilities lead to better customer interactions and satisfaction.
- Increased Scalability and Flexibility: ERP systems can grow with the business, providing the flexibility needed to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Better Supply Chain Management: Improved inventory control and procurement processes lead to a more efficient supply chain.
- Enhanced Human Resources Management: Streamlined HR processes result in better employee productivity and satisfaction.
- Operational Efficiency: ERP systems significantly enhance operational efficiency by integrating various business processes into a single unified system.
ERP System Components
An ERP system is composed of several key components, each designed to manage specific business functions. These components include:
- Financial Management: This module handles all financial planning, transactions, accounting, and reporting, ensuring accurate financial data and compliance with regulations.
- Human Resource Management: This component manages employee data, payroll, benefits, and other HR-related tasks, promoting a more efficient workforce.
- Supply Chain Management: This module oversees inventory, procurement, and logistics, ensuring a smooth and efficient supply chain.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): This component manages customer interactions, sales, and service, helping to build stronger customer relationships.
- Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP): This module focuses on production planning, scheduling, and control, optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Enterprise Asset Management: This component manages the maintenance, repair, and operations of physical assets, ensuring they are kept in optimal condition.

Simplifying Core Business Processes
ERP systems streamline core business processes by providing an integrated management solution. Through process automation, discrepancies are reduced and operations become smoother. This is vital in ensuring business growth and maintaining a competitive edge.
Integrating Business Functions
ERP technology is designed to integrate various business functions, from human resource management and financial reporting to supply chain management and customer relationship management (CRM). Data integration within a unified software system like a cloud-based ERP offers a centralized system that eliminates the need for disparate systems, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Improving Financial Management
Financial planning is a crucial aspect of ERP solutions, as it provides real-time insights into financial performance. These insights allow for better strategic planning and decision-making. By automating financial reports and ensuring regulatory compliance, ERPs allow the accounting team to focus on more value-added activities.
Elevating Supply Chain Management
ERP systems offer comprehensive modules for supply chain management, from production planning to inventory management systems. These tools help in synchronizing supply chain operations, reducing costs, and improving supplier relationship management.
Enhancing Customer Relationship Management
Modern ERP solutions include CRM functionalities, which empower businesses to improve their interactions with customers by leveraging customer data. By offering detailed insights into customer behavior and preferences, CRM in ERP systems helps to foster more meaningful relationships with customers.
Facilitating Human Resource Management
Human resources are a critical component of any organization. ERP software offers modules that help manage all human resource aspects from recruiting and training to payroll and benefits administration, thus promoting a more productive and happy workforce.
Offering Real-time Business Intelligence
ERP systems provide business leaders with actionable insights through data analytics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and business intelligence. This empowers leaders to make data-driven decisions that align with company objectives.
ERP Security and Compliance
Ensuring robust security and compliance is crucial for ERP systems, as they handle sensitive business data. Key security and compliance measures include:
- Data Encryption and Access Controls: Protecting data through encryption and restricting access to authorized personnel only.
- Regular Software Updates and Patches: Keeping the ERP system up-to-date with the latest security patches to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Compliance with Industry-Specific Regulations: Adhering to regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA to ensure data privacy and security.
- Implementation of Security Protocols: Utilizing protocols like two-factor authentication and firewalls to enhance security.
- Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments: Conducting periodic audits and assessments to identify and mitigate potential security risks.
- Training and Awareness Programs: Educating employees on security best practices to prevent breaches and ensure compliance.
By implementing these measures, businesses can safeguard their ERP systems and ensure they remain compliant with industry standards, protecting their valuable data and maintaining operational integrity.
Implementing a New ERP System
The ERP implementation process is a crucial phase. Whether migrating data from an existing ERP system or starting fresh, it involves a comprehensive approach, from selecting an ERP vendor to project management and data migration. ERP implementation can be a complex process, but when done right, the rewards in terms of operational efficiency are substantial.
Ensuring Mobile Accessibility
With the advent of mobile devices, modern ERP solutions, including mobile ERP, are designed to be accessible on the go. This adds flexibility for employees and ensures that key company data can be accessed anytime, anywhere.
The Future: Cloud ERP and SaaS Models
As businesses continue to evolve, so does ERP technology. Cloud computing plays a crucial role in the scalability and cost-effectiveness of ERP models. Cloud ERP and Software as a Service (SaaS) ERP models are increasingly popular due to their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the reduced burden they place on a company’s IT resources.
Choosing the Right ERP Software
Choosing the right ERP software is a critical decision for any organization. With a plethora of options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which one is best suited for your business. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting an ERP software:
- Business Needs: Start by identifying your organization’s specific needs and requirements. What are your core business processes? What pain points are you looking to address? Understanding these aspects will help you choose an ERP solution that aligns with your operational goals.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the ERP software. As your business grows, your ERP system should be able to grow with it. Ensure that the software can handle increased data volume and user load without compromising performance.
- Customization: Determine the level of customization required. Can the software be tailored to meet your specific needs? A flexible ERP system that allows for customization can better support your unique business processes.
- Integration: Evaluate the integration requirements. Will the software integrate seamlessly with your existing systems and software? An ERP solution that offers robust integration capabilities can streamline operations and reduce data silos.
- Cost: Assess the total cost of ownership. This includes upfront costs, maintenance costs, and support costs. Ensure that the ERP software provides value for money and fits within your budget.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s reputation. What is their track record? What do their customers say about them? A reputable ERP vendor with positive customer feedback is more likely to provide reliable and effective solutions.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose the right ERP software for your organization, ensuring that it supports and enhances your core business processes.
Measuring ERP Performance and ROI
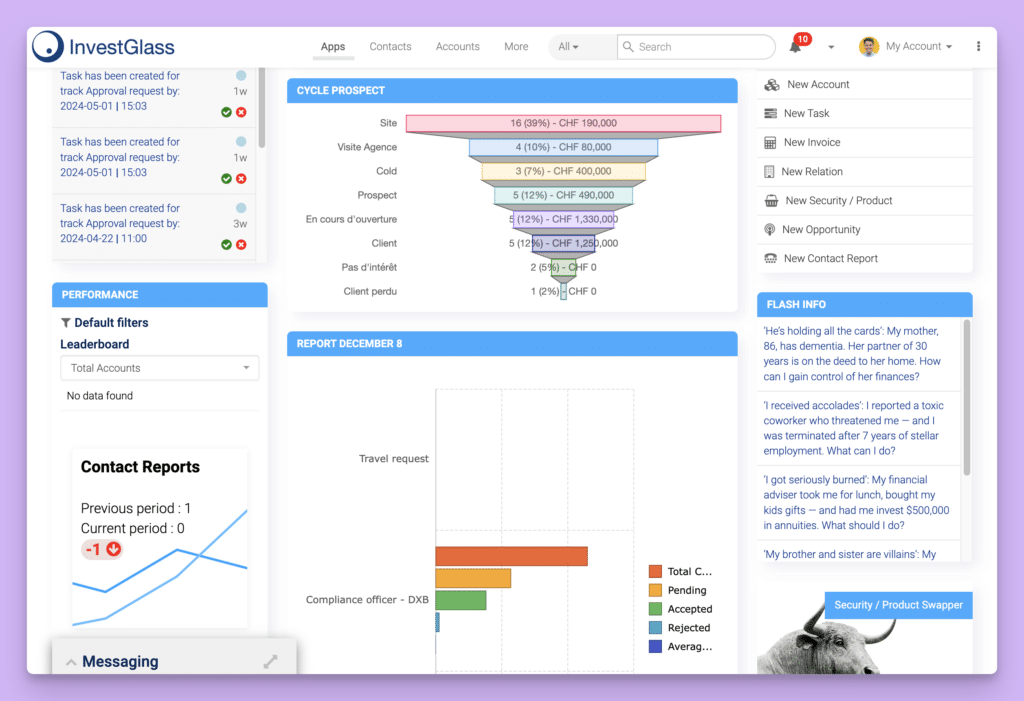
Measuring the performance and return on investment (ROI) of an ERP system is crucial to determining its effectiveness and value to your organization. Here are some key metrics to consider:
- Cost Savings: Evaluate the cost savings achieved through process automation, reduced manual errors, and improved efficiency. An effective ERP system should help lower operational costs and increase profitability.
- Increased Productivity: Measure the increase in productivity achieved through streamlined processes and improved workflows. Enhanced productivity is a clear indicator of the ERP system’s positive impact on your business operations.
- Improved Decision-Making: Assess the improvement in decision-making achieved through real-time data and analytics. An ERP system that provides accurate and timely information enables better strategic planning and quicker responses to market changes.
- Customer Satisfaction: Measure the improvement in customer satisfaction achieved through enhanced customer service and support. A robust ERP system with integrated customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities can lead to better customer interactions and loyalty.
- Return on Investment: Calculate the ROI of the ERP system by comparing the costs to the benefits achieved. This includes both tangible benefits like cost savings and intangible benefits like improved employee morale and customer satisfaction.
By tracking these metrics, you can determine the effectiveness of your ERP system and make data-driven decisions to improve its performance, ensuring that it continues to deliver value to your organization.
Industry-Specific ERP Applications
ERP systems can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries, providing specialized functionalities that address unique business challenges. Here are some examples of industry-specific ERP applications:
- Manufacturing: ERP systems for manufacturing can help manage production planning, inventory control, and supply chain management. These systems optimize manufacturing resource planning (MRP), ensuring efficient production processes and timely delivery of products.
- Retail: ERP systems for retail can help manage inventory management, point of sale (POS), and customer relationship management (CRM). By integrating these functions, retail businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and improve customer experiences.
- Healthcare: ERP systems for healthcare can help manage patient records, billing, and supply chain management. These systems ensure compliance with healthcare regulations, streamline administrative tasks, and improve patient care.
- Finance: ERP systems for finance can help manage financial planning, accounting, and risk management. By providing real-time financial data and analytics, these systems support better decision-making and regulatory compliance.
By selecting an ERP system that is tailored to your industry, you can ensure that it meets your specific needs and requirements, enhancing your business processes and overall performance.
Team Collaboration and ERP
ERP systems can significantly enhance team collaboration by providing a centralized platform for data sharing and communication. Here are some ways ERP systems can support team collaboration:
- Real-Time Data Sharing: ERP systems offer real-time data sharing, enabling teams to access the same information simultaneously. This ensures that everyone is on the same page, facilitating informed decision-making and reducing the risk of errors.
- Collaborative Workflows: ERP systems support collaborative workflows, allowing teams to work together on projects and tasks seamlessly. By automating and streamlining workflows, ERP systems enhance productivity and ensure that tasks are completed efficiently.
- Communication Tools: ERP systems often include communication tools such as messaging and email, which facilitate communication between team members. These tools help teams stay connected, share updates, and collaborate effectively, regardless of their physical location.
- Role-Based Access: ERP systems provide role-based access, enabling teams to control who has access to specific data and functions. This ensures that sensitive information is protected while allowing team members to access the data they need to perform their roles effectively.
By leveraging these features, teams can work more effectively together, achieve their goals, and drive business success. ERP systems not only streamline business processes but also foster a collaborative work environment, enhancing overall organizational performance.
InvestGlass: A Superior ERP Solution for Growth-Driven Firms
In an era where enterprise resource planning systems are integral to efficient business operations, InvestGlass is making a name for itself as a superior ERP solution for growing firms by leveraging business intelligence tools for streamlined workflows. Unlike early ERP systems that were often rigid and challenging to integrate with an existing system, InvestGlass leverages approval process automation, artificial intelligence, and state-of-the-art enterprise resource planning software technology. For example, InvestGlass’ intelligent approval process empowers companies with streamlined workflows, which ultimately reduces operational costs. With modern manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) capabilities, InvestGlass enables businesses to manage production processes and inventory management systems efficiently. This holistic approach not only helps in reducing costs but also optimizes product lifecycle management. Additionally, InvestGlass offers a variety of ERP deployment models, making it adaptable and scalable for businesses of different sizes and industries. Furthermore, the process of implementing ERP projects with InvestGlass is designed to be as seamless as possible, from selecting from a range of trusted ERP providers and vendors to ensuring that the software aligns with best business practices. In a marketplace crowded with ERP modules and options, InvestGlass offers intelligent, automated, and highly customizable solutions that meet the nuanced needs of growing firms in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Learn more
Why is continuous improvement crucial for maintaining an effective ERP manufacturing process?
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, continuous improvement is not just a choice—it’s essential for survival. This approach focuses on making ongoing, incremental enhancements to products, services, or processes rather than waiting for the periodic overhaul. Here’s why it matters for your ERP manufacturing process:
1. Sustained Growth and Efficiency
- Incremental Progress: Making small, regular improvements leads to consistent growth and operational efficiency, which in turn boosts productivity.
- Resource Optimization: By refining processes gradually, manufacturers can better allocate resources, reducing waste and maximizing profits.
2. Agility and Adaptability
- Market Responsiveness: A flexible ERP setup allows your business to quickly adapt to fluctuating market demands.
- Technological Integration: Continuous improvement ensures that your systems evolve alongside technological advancements, keeping your operations up-to-date.
3. Competitive Advantage
- Staying Ahead: Regular improvements can set your manufacturing process apart from competitors, establishing your brand as a leader in the industry.
- Customer Satisfaction: By enhancing your processes continuously, you’re better positioned to meet customer expectations, which can lead to increased loyalty and sales.
In conclusion, embedding a culture of continuous improvement into your ERP manufacturing process is paramount. It drives efficiency, fosters agility, and helps maintain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving market.
What Are Common Bottlenecks in the ERP Manufacturing Process?
In the intricate dance of manufacturing, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems play a crucial role in streamlining operations. Yet, even with technological advancements, bottlenecks can arise, impeding the flow of production. Here, we explore some prevalent hurdles faced in the ERP manufacturing process:
Production Delays
Bottlenecks often surface when certain production stages falter, causing a ripple effect across operations. If a machine demands frequent maintenance or functions at a slower rate compared to others, it can stall the entire production line. Such delays not only affect schedules but also escalate operational costs.
Inefficient Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is pivotal in avoiding excess inventory or out-of-stock scenarios. Overloading inventory unnecessarily ties up capital, while a shortage can grind production to a halt. Both extremes disrupt the seamless flow of materials, delay production timelines, and impact revenue.

Absence of Real-Time Data
Having access to real-time data is critical for informed decision-making. When data is inaccurate or outdated, it hinders the ability to promptly identify and resolve issues within the ERP system. This lack of visibility leads to inefficiencies, as it’s difficult to determine where and when production obstacles arise.
Inadequate Communication Channels
Communication breakdowns between teams or departments can significantly slow down production. When vital information isn’t shared promptly, it generates misunderstandings and errors. These lapses can cause unnecessary delays, impacting the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
These bottlenecks highlight the need for robust ERP solutions that enhance transparency, improve coordination, and streamline operations to ensure a fluid and efficient manufacturing process.
How to apply Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Kaizen to ERP Processes?
Optimizing ERP processes is essential for enhancing efficiency and quality in manufacturing. Three methodologies—Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Kaizen—offer robust frameworks for driving continuous improvement and can be effectively applied to ERP systems. Incorporating value stream mapping into these methodologies can further streamline ERP processes.
Lean Manufacturing: Streamlining and Efficiency
Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste while enhancing productivity. When applied to ERP processes, this approach can streamline production workflows and reduce unnecessary activities. For example:
- Streamlined Workflows: Simplify production processes by removing redundant steps, ensuring that ERP systems facilitate faster and more efficient operations.
- Inventory Optimization: Reduce excess inventory by utilizing ERP tools to maintain just-in-time stock levels, minimizing costs.
- Waste Elimination: Identify and eliminate non-value-added tasks in ERP functions, creating a leaner and more agile operation.
Six Sigma: Quality and Precision
Six Sigma methodologies aim to minimize defects and variability. Integrating Six Sigma into ERP processes involves using data-driven strategies to enhance overall system quality and reliability:
- Data Analysis: Employ statistical tools within the ERP to pinpoint and resolve inefficiencies, thus improving the accuracy of operations.
- Process Standardization: Establish uniform procedures and metrics within the ERP to maintain high-quality outputs and minimize errors.
- Customer Satisfaction: Improve product and service quality, directly benefiting customer experience and satisfaction.
Kaizen: Continuous Improvement and Employee Engagement
Kaizen focuses on ongoing improvement and involves every employee in the enhancement of processes. Incorporating Kaizen in ERP systems encourages a continuous evolution of processes:
- Collaborative Meetings: Host regular sessions where teams review ERP workflows, identifying opportunities for incremental improvements.
- Culture of Innovation: Foster an environment where every team member contributes ideas to enhance ERP functionality and service.
- Adaptation: Encourage agility within the ERP system to quickly adapt to industry changes and new challenges.
By applying these methodologies, ERP systems become more efficient, precise, and adaptive, leading to improved overall performance and competitive advantage.
Value stream mapping (VSM) and workflow analysis are essential techniques for uncovering bottlenecks in manufacturing processes. Here’s how each contributes to streamlining production:
Do you know what is Value Stream Mapping (VSM)?
VSM is an invaluable tool that provides a visual representation of your entire manufacturing process. This visualization covers everything from the intake of raw materials to the delivery of finished products. By mapping each stage, VSM helps identify delays and inefficiencies that may not be apparent at first glance. This comprehensive view enables you to spot which steps are causing slowdowns, allowing you to target and optimize these critical areas effectively.
Workflow Analysis
Workflow analysis delves deeper into examining each step of your production process. It’s all about dissecting the workflow to uncover hidden inefficiencies. By analyzing these processes meticulously, you can identify specific points where bottlenecks occur. Once these are pinpointed, you can investigate their root causes, which might include equipment malfunctions, staffing issues, or procedural errors.
Through both VSM and workflow analysis, companies can gain a clearer perspective on their operations. These methodologies do more than surface-level diagnostics—they uncover the underlying issues that, when addressed, can significantly enhance efficiency and productivity in the manufacturing process.
What is the Role of ERP in Business Process? A Look at InvestGlass Optimization
In today’s fast-paced business environment, efficient operations management across the entire organization is essential for success. Digital transformation is a key driver in modernizing these operations. This is where an enterprise resource planning system becomes a game-changer. By integrating critical functions such as inventory management systems, finance, human resources, and more, ERP systems enable businesses to streamline processes and enhance productivity. ERP vendors continually innovate to provide solutions that help organisations reduce costs and optimize workflows. But how exactly does an enterprise resource planning system refine business processes to benefit the organization? InvestGalss offers a full inventory management system hosted in Switzerland or on-premise. Let’s explore this in detail.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a powerful business management software that integrates all aspects of an organization’s operations into a unified system. By providing real-time visibility into the inner workings of a business, ERP systems help automate and streamline back-office tasks, enabling employees to become more productive and successful in their roles. These systems are designed to manage and integrate various business functions, including financial management, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management (CRM). With an ERP system, businesses can ensure that all departments are working with the same data, reducing discrepancies and enhancing overall efficiency.
Benefits of ERP Systems
ERP systems offer a multitude of benefits to organizations, making them an invaluable tool for business process optimization. Some of the key advantages include:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: By automating routine tasks and providing a centralized data repository, ERP systems help streamline operations and reduce manual effort.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: With real-time data and analytics, business leaders can make informed decisions quickly and accurately.
- Reduced Costs: ERP systems help in better financial management, reducing operational costs and improving profitability.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Enhanced customer relationship management capabilities lead to better customer interactions and satisfaction.
- Increased Scalability and Flexibility: ERP systems can grow with the business, providing the flexibility needed to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Better Supply Chain Management: Improved inventory control and procurement processes lead to a more efficient supply chain.
- Enhanced Human Resources Management: Streamlined HR processes result in better employee productivity and satisfaction.
- Operational Efficiency: ERP systems significantly enhance operational efficiency by integrating various business processes into a single unified system.
ERP System Components
An ERP system is composed of several key components, each designed to manage specific business functions. These components include:
- Financial Management: This module handles all financial planning, transactions, accounting, and reporting, ensuring accurate financial data and compliance with regulations.
- Human Resource Management: This component manages employee data, payroll, benefits, and other HR-related tasks, promoting a more efficient workforce.
- Supply Chain Management: This module oversees inventory, procurement, and logistics, ensuring a smooth and efficient supply chain.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): This component manages customer interactions, sales, and service, helping to build stronger customer relationships.
- Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP): This module focuses on production planning, scheduling, and control, optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Enterprise Asset Management: This component manages the maintenance, repair, and operations of physical assets, ensuring they are kept in optimal condition.
Simplifying Core Business Processes
ERP systems streamline core business processes by providing an integrated management solution. Through process automation, discrepancies are reduced and operations become smoother. This is vital in ensuring business growth and maintaining a competitive edge.
Integrating Business Functions
ERP technology is designed to integrate various business functions, from human resource management and financial reporting to supply chain management and customer relationship management (CRM). Data integration within a unified software system like a cloud-based ERP offers a centralized system that eliminates the need for disparate systems, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Improving Financial Management
Financial planning is a crucial aspect of ERP solutions, as it provides real-time insights into financial performance. These insights allow for better strategic planning and decision-making. By automating financial reports and ensuring regulatory compliance, ERPs allow the accounting team to focus on more value-added activities.
Elevating Supply Chain Management
ERP systems offer comprehensive modules for supply chain management, from production planning to inventory management systems. These tools help in synchronizing supply chain operations, reducing costs, and improving supplier relationship management.
Enhancing Customer Relationship Management
Modern ERP solutions include CRM functionalities, which empower businesses to improve their interactions with customers by leveraging customer data. By offering detailed insights into customer behavior and preferences, CRM in ERP systems helps to foster more meaningful relationships with customers.
Facilitating Human Resource Management
Human resources are a critical component of any organization. ERP software offers modules that help manage all human resource aspects from recruiting and training to payroll and benefits administration, thus promoting a more productive and happy workforce.
Offering Real-time Business Intelligence
ERP systems provide business leaders with actionable insights through data analytics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and business intelligence. This empowers leaders to make data-driven decisions that align with company objectives.
ERP Security and Compliance
Ensuring robust security and compliance is crucial for ERP systems, as they handle sensitive business data. Key security and compliance measures include:
- Data Encryption and Access Controls: Protecting data through encryption and restricting access to authorized personnel only.
- Regular Software Updates and Patches: Keeping the ERP system up-to-date with the latest security patches to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Compliance with Industry-Specific Regulations: Adhering to regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA to ensure data privacy and security.
- Implementation of Security Protocols: Utilizing protocols like two-factor authentication and firewalls to enhance security.
- Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments: Conducting periodic audits and assessments to identify and mitigate potential security risks.
- Training and Awareness Programs: Educating employees on security best practices to prevent breaches and ensure compliance.
By implementing these measures, businesses can safeguard their ERP systems and ensure they remain compliant with industry standards, protecting their valuable data and maintaining operational integrity.
Implementing a New ERP System
The ERP implementation process is a crucial phase. Whether migrating data from an existing ERP system or starting fresh, it involves a comprehensive approach, from selecting an ERP vendor to project management and data migration. ERP implementation can be a complex process, but when done right, the rewards in terms of operational efficiency are substantial.

Ensuring Mobile Accessibility
With the advent of mobile devices, modern ERP solutions, including mobile ERP, are designed to be accessible on the go. This adds flexibility for employees and ensures that key company data can be accessed anytime, anywhere.
The Future: Cloud ERP and SaaS Models
As businesses continue to evolve, so does ERP technology. Cloud computing plays a crucial role in the scalability and cost-effectiveness of ERP models. Cloud ERP and Software as a Service (SaaS) ERP models are increasingly popular due to their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the reduced burden they place on a company’s IT resources.
Choosing the Right ERP Software
Choosing the right ERP software is a critical decision for any organization. With a plethora of options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which one is best suited for your business. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting an ERP software:
- Business Needs: Start by identifying your organization’s specific needs and requirements. What are your core business processes? What pain points are you looking to address? Understanding these aspects will help you choose an ERP solution that aligns with your operational goals.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the ERP software. As your business grows, your ERP system should be able to grow with it. Ensure that the software can handle increased data volume and user load without compromising performance.
- Customization: Determine the level of customization required. Can the software be tailored to meet your specific needs? A flexible ERP system that allows for customization can better support your unique business processes.
- Integration: Evaluate the integration requirements. Will the software integrate seamlessly with your existing systems and software? An ERP solution that offers robust integration capabilities can streamline operations and reduce data silos.
- Cost: Assess the total cost of ownership. This includes upfront costs, maintenance costs, and support costs. Ensure that the ERP software provides value for money and fits within your budget.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s reputation. What is their track record? What do their customers say about them? A reputable ERP vendor with positive customer feedback is more likely to provide reliable and effective solutions.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose the right ERP software for your organization, ensuring that it supports and enhances your core business processes.
Measuring ERP Performance and ROI
Measuring the performance and return on investment (ROI) of an ERP system is crucial to determining its effectiveness and value to your organization. Here are some key metrics to consider:
- Cost Savings: Evaluate the cost savings achieved through process automation, reduced manual errors, and improved efficiency. An effective ERP system should help lower operational costs and increase profitability.
- Increased Productivity: Measure the increase in productivity achieved through streamlined processes and improved workflows. Enhanced productivity is a clear indicator of the ERP system’s positive impact on your business operations.
- Improved Decision-Making: Assess the improvement in decision-making achieved through real-time data and analytics. An ERP system that provides accurate and timely information enables better strategic planning and quicker responses to market changes.
- Customer Satisfaction: Measure the improvement in customer satisfaction achieved through enhanced customer service and support. A robust ERP system with integrated customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities can lead to better customer interactions and loyalty.
- Return on Investment: Calculate the ROI of the ERP system by comparing the costs to the benefits achieved. This includes both tangible benefits like cost savings and intangible benefits like improved employee morale and customer satisfaction.
By tracking these metrics, you can determine the effectiveness of your ERP system and make data-driven decisions to improve its performance, ensuring that it continues to deliver value to your organization.
Industry-Specific ERP Applications
ERP systems can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries, providing specialized functionalities that address unique business challenges. Here are some examples of industry-specific ERP applications:
- Manufacturing: ERP systems for manufacturing can help manage production planning, inventory control, and supply chain management. These systems optimize manufacturing resource planning (MRP), ensuring efficient production processes and timely delivery of products.
- Retail: ERP systems for retail can help manage inventory management, point of sale (POS), and customer relationship management (CRM). By integrating these functions, retail businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and improve customer experiences.
- Healthcare: ERP systems for healthcare can help manage patient records, billing, and supply chain management. These systems ensure compliance with healthcare regulations, streamline administrative tasks, and improve patient care.
- Finance: ERP systems for finance can help manage financial planning, accounting, and risk management. By providing real-time financial data and analytics, these systems support better decision-making and regulatory compliance.
By selecting an ERP system that is tailored to your industry, you can ensure that it meets your specific needs and requirements, enhancing your business processes and overall performance.
Team Collaboration and ERP
ERP systems can significantly enhance team collaboration by providing a centralized platform for data sharing and communication. Here are some ways ERP systems can support team collaboration:
- Real-Time Data Sharing: ERP systems offer real-time data sharing, enabling teams to access the same information simultaneously. This ensures that everyone is on the same page, facilitating informed decision-making and reducing the risk of errors.
- Collaborative Workflows: ERP systems support collaborative workflows, allowing teams to work together on projects and tasks seamlessly. By automating and streamlining workflows, ERP systems enhance productivity and ensure that tasks are completed efficiently.
- Communication Tools: ERP systems often include communication tools such as messaging and email, which facilitate communication between team members. These tools help teams stay connected, share updates, and collaborate effectively, regardless of their physical location.
- Role-Based Access: ERP systems provide role-based access, enabling teams to control who has access to specific data and functions. This ensures that sensitive information is protected while allowing team members to access the data they need to perform their roles effectively.
By leveraging these features, teams can work more effectively together, achieve their goals, and drive business success. ERP systems not only streamline business processes but also foster a collaborative work environment, enhancing overall organizational performance.
InvestGlass: A Superior ERP Solution for Growth-Driven Firms
In an era where enterprise resource planning systems are integral to efficient business operations, InvestGlass is making a name for itself as a superior ERP solution for growing firms by leveraging business intelligence tools for streamlined workflows. Unlike early ERP systems that were often rigid and challenging to integrate with an existing system, InvestGlass leverages approval process automation, artificial intelligence, and state-of-the-art enterprise resource planning software technology. For example, InvestGlass’ intelligent approval process empowers companies with streamlined workflows, which ultimately reduces operational costs. With modern manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) capabilities, InvestGlass enables businesses to manage production processes and inventory management systems efficiently. This holistic approach not only helps in reducing costs but also optimizes product lifecycle management. Additionally, InvestGlass offers a variety of ERP deployment models, making it adaptable and scalable for businesses of different sizes and industries. Furthermore, the process of implementing ERP projects with InvestGlass is designed to be as seamless as possible, from selecting from a range of trusted ERP providers and vendors to ensuring that the software aligns with best business practices. In a marketplace crowded with ERP modules and options, InvestGlass offers intelligent, automated, and highly customizable solutions that meet the nuanced needs of growing firms in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Your successful ERP systems strategy with InvestGlass
In conclusion, digital transformation through ERP systems is more than just business management software; it is a strategic investment for any business aiming for growth and efficiency. By integrating and automating key business functions, an ERP solution can transform the entire business, aiding in achieving better business performance and setting the foundation for a bright, sustainable future.
The decision to transition to a new system, especially a new ERP system, is significant. But with the right ERP vendor and a careful implementation process, businesses can navigate this change successfully and set themselves up for long-term success.
Remember, as with any enterprise system, the ERP life cycle is ongoing; regular updates and improvements are key to ensuring that the ERP solution continues to meet the needs of the evolving business landscape.
Learn more
Why is continuous improvement crucial for maintaining an effective ERP manufacturing process?
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, continuous improvement is not just a choice—it’s essential for survival. This approach focuses on making ongoing, incremental enhancements to products, services, or processes rather than waiting for the periodic overhaul. Here’s why it matters for your ERP manufacturing process:
1. Sustained Growth and Efficiency
- Incremental Progress: Making small, regular improvements leads to consistent growth and operational efficiency, which in turn boosts productivity.
- Resource Optimization: By refining processes gradually, manufacturers can better allocate resources, reducing waste and maximizing profits.
2. Agility and Adaptability
- Market Responsiveness: A flexible ERP setup allows your business to quickly adapt to fluctuating market demands.
- Technological Integration: Continuous improvement ensures that your systems evolve alongside technological advancements, keeping your operations up-to-date.
3. Competitive Advantage
- Staying Ahead: Regular improvements can set your manufacturing process apart from competitors, establishing your brand as a leader in the industry.
- Customer Satisfaction: By enhancing your processes continuously, you’re better positioned to meet customer expectations, which can lead to increased loyalty and sales.
In conclusion, embedding a culture of continuous improvement into your ERP manufacturing process is paramount. It drives efficiency, fosters agility, and helps maintain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving market.
What Are Common Bottlenecks in the ERP Manufacturing Process?
In the intricate dance of manufacturing, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems play a crucial role in streamlining operations. Yet, even with technological advancements, bottlenecks can arise, impeding the flow of production. Here, we explore some prevalent hurdles faced in the ERP manufacturing process:
Production Delays
Bottlenecks often surface when certain production stages falter, causing a ripple effect across operations. If a machine demands frequent maintenance or functions at a slower rate compared to others, it can stall the entire production line. Such delays not only affect schedules but also escalate operational costs.
Inefficient Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is pivotal in avoiding excess inventory or out-of-stock scenarios. Overloading inventory unnecessarily ties up capital, while a shortage can grind production to a halt. Both extremes disrupt the seamless flow of materials, delay production timelines, and impact revenue.
Absence of Real-Time Data
Having access to real-time data is critical for informed decision-making. When data is inaccurate or outdated, it hinders the ability to promptly identify and resolve issues within the ERP system. This lack of visibility leads to inefficiencies, as it’s difficult to determine where and when production obstacles arise.
Inadequate Communication Channels
Communication breakdowns between teams or departments can significantly slow down production. When vital information isn’t shared promptly, it generates misunderstandings and errors. These lapses can cause unnecessary delays, impacting the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
These bottlenecks highlight the need for robust ERP solutions that enhance transparency, improve coordination, and streamline operations to ensure a fluid and efficient manufacturing process.
How to apply Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Kaizen to ERP Processes?
Optimizing ERP processes is essential for enhancing efficiency and quality in manufacturing. Three methodologies—Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Kaizen—offer robust frameworks for driving continuous improvement and can be effectively applied to ERP systems. Incorporating value stream mapping into these methodologies can further streamline ERP processes.
Lean Manufacturing: Streamlining and Efficiency
Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste while enhancing productivity. When applied to ERP processes, this approach can streamline production workflows and reduce unnecessary activities. For example:
- Streamlined Workflows: Simplify production processes by removing redundant steps, ensuring that ERP systems facilitate faster and more efficient operations.
- Inventory Optimization: Reduce excess inventory by utilizing ERP tools to maintain just-in-time stock levels, minimizing costs.
- Waste Elimination: Identify and eliminate non-value-added tasks in ERP functions, creating a leaner and more agile operation.
Six Sigma: Quality and Precision
Six Sigma methodologies aim to minimize defects and variability. Integrating Six Sigma into ERP processes involves using data-driven strategies to enhance overall system quality and reliability:
- Data Analysis: Employ statistical tools within the ERP to pinpoint and resolve inefficiencies, thus improving the accuracy of operations.
- Process Standardization: Establish uniform procedures and metrics within the ERP to maintain high-quality outputs and minimize errors.
- Customer Satisfaction: Improve product and service quality, directly benefiting customer experience and satisfaction.
Kaizen: Continuous Improvement and Employee Engagement
Kaizen focuses on ongoing improvement and involves every employee in the enhancement of processes. Incorporating Kaizen in ERP systems encourages a continuous evolution of processes:
- Collaborative Meetings: Host regular sessions where teams review ERP workflows, identifying opportunities for incremental improvements.
- Culture of Innovation: Foster an environment where every team member contributes ideas to enhance ERP functionality and service.
- Adaptation: Encourage agility within the ERP system to quickly adapt to industry changes and new challenges.
By applying these methodologies, ERP systems become more efficient, precise, and adaptive, leading to improved overall performance and competitive advantage.
Value stream mapping (VSM) and workflow analysis are essential techniques for uncovering bottlenecks in manufacturing processes. Here’s how each contributes to streamlining production:
Do you know what is Value Stream Mapping (VSM)?
VSM is an invaluable tool that provides a visual representation of your entire manufacturing process. This visualization covers everything from the intake of raw materials to the delivery of finished products. By mapping each stage, VSM helps identify delays and inefficiencies that may not be apparent at first glance. This comprehensive view enables you to spot which steps are causing slowdowns, allowing you to target and optimize these critical areas effectively.
Workflow Analysis
Workflow analysis delves deeper into examining each step of your production process. It’s all about dissecting the workflow to uncover hidden inefficiencies. By analyzing these processes meticulously, you can identify specific points where bottlenecks occur. Once these are pinpointed, you can investigate their root causes, which might include equipment malfunctions, staffing issues, or procedural errors.
Through both VSM and workflow analysis, companies can gain a clearer perspective on their operations. These methodologies do more than surface-level diagnostics—they uncover the underlying issues that, when addressed, can significantly enhance efficiency and productivity in the manufacturing process.
What is the Role of ERP in Business Process? A Look at InvestGlass Optimization
In today’s fast-paced business environment, efficient operations management across the entire organization is essential for success. Digital transformation is a key driver in modernizing these operations. This is where an enterprise resource planning system becomes a game-changer. By integrating critical functions such as inventory management systems, finance, human resources, and more, ERP systems enable businesses to streamline processes and enhance productivity. ERP vendors continually innovate to provide solutions that help organisations reduce costs and optimize workflows. But how exactly does an enterprise resource planning system refine business processes to benefit the organization? InvestGalss offers a full inventory management system hosted in Switzerland or on-premise. Let’s explore this in detail.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a powerful business management software that integrates all aspects of an organization’s operations into a unified system. By providing real-time visibility into the inner workings of a business, ERP systems help automate and streamline back-office tasks, enabling employees to become more productive and successful in their roles. These systems are designed to manage and integrate various business functions, including financial management, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management (CRM). With an ERP system, businesses can ensure that all departments are working with the same data, reducing discrepancies and enhancing overall efficiency.
Benefits of ERP Systems
ERP systems offer a multitude of benefits to organizations, making them an invaluable tool for business process optimization. Some of the key advantages include:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: By automating routine tasks and providing a centralized data repository, ERP systems help streamline operations and reduce manual effort.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: With real-time data and analytics, business leaders can make informed decisions quickly and accurately.
- Reduced Costs: ERP systems help in better financial management, reducing operational costs and improving profitability.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Enhanced customer relationship management capabilities lead to better customer interactions and satisfaction.
- Increased Scalability and Flexibility: ERP systems can grow with the business, providing the flexibility needed to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Better Supply Chain Management: Improved inventory control and procurement processes lead to a more efficient supply chain.
- Enhanced Human Resources Management: Streamlined HR processes result in better employee productivity and satisfaction.
- Operational Efficiency: ERP systems significantly enhance operational efficiency by integrating various business processes into a single unified system.
ERP System Components
An ERP system is composed of several key components, each designed to manage specific business functions. These components include:
- Financial Management: This module handles all financial planning, transactions, accounting, and reporting, ensuring accurate financial data and compliance with regulations.
- Human Resource Management: This component manages employee data, payroll, benefits, and other HR-related tasks, promoting a more efficient workforce.
- Supply Chain Management: This module oversees inventory, procurement, and logistics, ensuring a smooth and efficient supply chain.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): This component manages customer interactions, sales, and service, helping to build stronger customer relationships.
- Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP): This module focuses on production planning, scheduling, and control, optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Enterprise Asset Management: This component manages the maintenance, repair, and operations of physical assets, ensuring they are kept in optimal condition.
Simplifying Core Business Processes
ERP systems streamline core business processes by providing an integrated management solution. Through process automation, discrepancies are reduced and operations become smoother. This is vital in ensuring business growth and maintaining a competitive edge.
Integrating Business Functions
ERP technology is designed to integrate various business functions, from human resource management and financial reporting to supply chain management and customer relationship management (CRM). Data integration within a unified software system like a cloud-based ERP offers a centralized system that eliminates the need for disparate systems, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Improving Financial Management
Financial planning is a crucial aspect of ERP solutions, as it provides real-time insights into financial performance. These insights allow for better strategic planning and decision-making. By automating financial reports and ensuring regulatory compliance, ERPs allow the accounting team to focus on more value-added activities.
Elevating Supply Chain Management
ERP systems offer comprehensive modules for supply chain management, from production planning to inventory management systems. These tools help in synchronizing supply chain operations, reducing costs, and improving supplier relationship management.
Enhancing Customer Relationship Management
Modern ERP solutions include CRM functionalities, which empower businesses to improve their interactions with customers by leveraging customer data. By offering detailed insights into customer behavior and preferences, CRM in ERP systems helps to foster more meaningful relationships with customers.
Facilitating Human Resource Management
Human resources are a critical component of any organization. ERP software offers modules that help manage all human resource aspects from recruiting and training to payroll and benefits administration, thus promoting a more productive and happy workforce.
Offering Real-time Business Intelligence
ERP systems provide business leaders with actionable insights through data analytics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and business intelligence. This empowers leaders to make data-driven decisions that align with company objectives.
ERP Security and Compliance
Ensuring robust security and compliance is crucial for ERP systems, as they handle sensitive business data. Key security and compliance measures include:
- Data Encryption and Access Controls: Protecting data through encryption and restricting access to authorized personnel only.
- Regular Software Updates and Patches: Keeping the ERP system up-to-date with the latest security patches to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Compliance with Industry-Specific Regulations: Adhering to regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA to ensure data privacy and security.
- Implementation of Security Protocols: Utilizing protocols like two-factor authentication and firewalls to enhance security.
- Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments: Conducting periodic audits and assessments to identify and mitigate potential security risks.
- Training and Awareness Programs: Educating employees on security best practices to prevent breaches and ensure compliance.
By implementing these measures, businesses can safeguard their ERP systems and ensure they remain compliant with industry standards, protecting their valuable data and maintaining operational integrity.
Implementing a New ERP System
The ERP implementation process is a crucial phase. Whether migrating data from an existing ERP system or starting fresh, it involves a comprehensive approach, from selecting an ERP vendor to project management and data migration. ERP implementation can be a complex process, but when done right, the rewards in terms of operational efficiency are substantial.
Ensuring Mobile Accessibility
With the advent of mobile devices, modern ERP solutions, including mobile ERP, are designed to be accessible on the go. This adds flexibility for employees and ensures that key company data can be accessed anytime, anywhere.
The Future: Cloud ERP and SaaS Models
As businesses continue to evolve, so does ERP technology. Cloud computing plays a crucial role in the scalability and cost-effectiveness of ERP models. Cloud ERP and Software as a Service (SaaS) ERP models are increasingly popular due to their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the reduced burden they place on a company’s IT resources.
Choosing the Right ERP Software
Choosing the right ERP software is a critical decision for any organization. With a plethora of options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which one is best suited for your business. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting an ERP software:
- Business Needs: Start by identifying your organization’s specific needs and requirements. What are your core business processes? What pain points are you looking to address? Understanding these aspects will help you choose an ERP solution that aligns with your operational goals.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the ERP software. As your business grows, your ERP system should be able to grow with it. Ensure that the software can handle increased data volume and user load without compromising performance.
- Customization: Determine the level of customization required. Can the software be tailored to meet your specific needs? A flexible ERP system that allows for customization can better support your unique business processes.
- Integration: Evaluate the integration requirements. Will the software integrate seamlessly with your existing systems and software? An ERP solution that offers robust integration capabilities can streamline operations and reduce data silos.
- Cost: Assess the total cost of ownership. This includes upfront costs, maintenance costs, and support costs. Ensure that the ERP software provides value for money and fits within your budget.
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s reputation. What is their track record? What do their customers say about them? A reputable ERP vendor with positive customer feedback is more likely to provide reliable and effective solutions.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and choose the right ERP software for your organization, ensuring that it supports and enhances your core business processes.
Measuring ERP Performance and ROI
Measuring the performance and return on investment (ROI) of an ERP system is crucial to determining its effectiveness and value to your organization. Here are some key metrics to consider:
- Cost Savings: Evaluate the cost savings achieved through process automation, reduced manual errors, and improved efficiency. An effective ERP system should help lower operational costs and increase profitability.
- Increased Productivity: Measure the increase in productivity achieved through streamlined processes and improved workflows. Enhanced productivity is a clear indicator of the ERP system’s positive impact on your business operations.
- Improved Decision-Making: Assess the improvement in decision-making achieved through real-time data and analytics. An ERP system that provides accurate and timely information enables better strategic planning and quicker responses to market changes.
- Customer Satisfaction: Measure the improvement in customer satisfaction achieved through enhanced customer service and support. A robust ERP system with integrated customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities can lead to better customer interactions and loyalty.
- Return on Investment: Calculate the ROI of the ERP system by comparing the costs to the benefits achieved. This includes both tangible benefits like cost savings and intangible benefits like improved employee morale and customer satisfaction.
By tracking these metrics, you can determine the effectiveness of your ERP system and make data-driven decisions to improve its performance, ensuring that it continues to deliver value to your organization.
Industry-Specific ERP Applications
ERP systems can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries, providing specialized functionalities that address unique business challenges. Here are some examples of industry-specific ERP applications:
- Manufacturing: ERP systems for manufacturing can help manage production planning, inventory control, and supply chain management. These systems optimize manufacturing resource planning (MRP), ensuring efficient production processes and timely delivery of products.
- Retail: ERP systems for retail can help manage inventory management, point of sale (POS), and customer relationship management (CRM). By integrating these functions, retail businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and improve customer experiences.
- Healthcare: ERP systems for healthcare can help manage patient records, billing, and supply chain management. These systems ensure compliance with healthcare regulations, streamline administrative tasks, and improve patient care.
- Finance: ERP systems for finance can help manage financial planning, accounting, and risk management. By providing real-time financial data and analytics, these systems support better decision-making and regulatory compliance.
By selecting an ERP system that is tailored to your industry, you can ensure that it meets your specific needs and requirements, enhancing your business processes and overall performance.
Team Collaboration and ERP
ERP systems can significantly enhance team collaboration by providing a centralized platform for data sharing and communication. Here are some ways ERP systems can support team collaboration:
- Real-Time Data Sharing: ERP systems offer real-time data sharing, enabling teams to access the same information simultaneously. This ensures that everyone is on the same page, facilitating informed decision-making and reducing the risk of errors.
- Collaborative Workflows: ERP systems support collaborative workflows, allowing teams to work together on projects and tasks seamlessly. By automating and streamlining workflows, ERP systems enhance productivity and ensure that tasks are completed efficiently.
- Communication Tools: ERP systems often include communication tools such as messaging and email, which facilitate communication between team members. These tools help teams stay connected, share updates, and collaborate effectively, regardless of their physical location.
- Role-Based Access: ERP systems provide role-based access, enabling teams to control who has access to specific data and functions. This ensures that sensitive information is protected while allowing team members to access the data they need to perform their roles effectively.
By leveraging these features, teams can work more effectively together, achieve their goals, and drive business success. ERP systems not only streamline business processes but also foster a collaborative work environment, enhancing overall organizational performance.
InvestGlass: A Superior ERP Solution for Growth-Driven Firms
In an era where enterprise resource planning systems are integral to efficient business operations, InvestGlass is making a name for itself as a superior ERP solution for growing firms by leveraging business intelligence tools for streamlined workflows. Unlike early ERP systems that were often rigid and challenging to integrate with an existing system, InvestGlass leverages approval process automation, artificial intelligence, and state-of-the-art enterprise resource planning software technology. For example, InvestGlass’ intelligent approval process empowers companies with streamlined workflows, which ultimately reduces operational costs. With modern manufacturing resource planning (MRP II) capabilities, InvestGlass enables businesses to manage production processes and inventory management systems efficiently. This holistic approach not only helps in reducing costs but also optimizes product lifecycle management. Additionally, InvestGlass offers a variety of ERP deployment models, making it adaptable and scalable for businesses of different sizes and industries. Furthermore, the process of implementing ERP projects with InvestGlass is designed to be as seamless as possible, from selecting from a range of trusted ERP providers and vendors to ensuring that the software aligns with best business practices. In a marketplace crowded with ERP modules and options, InvestGlass offers intelligent, automated, and highly customizable solutions that meet the nuanced needs of growing firms in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Learn more
Why is continuous improvement crucial for maintaining an effective ERP manufacturing process?
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, continuous improvement is not just a choice—it’s essential for survival. This approach focuses on making ongoing, incremental enhancements to products, services, or processes rather than waiting for the periodic overhaul. Here’s why it matters for your ERP manufacturing process:
1. Sustained Growth and Efficiency
- Incremental Progress: Making small, regular improvements leads to consistent growth and operational efficiency, which in turn boosts productivity.
- Resource Optimization: By refining processes gradually, manufacturers can better allocate resources, reducing waste and maximizing profits.
2. Agility and Adaptability
- Market Responsiveness: A flexible ERP setup allows your business to quickly adapt to fluctuating market demands.
- Technological Integration: Continuous improvement ensures that your systems evolve alongside technological advancements, keeping your operations up-to-date.
3. Competitive Advantage
- Staying Ahead: Regular improvements can set your manufacturing process apart from competitors, establishing your brand as a leader in the industry.
- Customer Satisfaction: By enhancing your processes continuously, you’re better positioned to meet customer expectations, which can lead to increased loyalty and sales.
In conclusion, embedding a culture of continuous improvement into your ERP manufacturing process is paramount. It drives efficiency, fosters agility, and helps maintain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving market.
What Are Common Bottlenecks in the ERP Manufacturing Process?
In the intricate dance of manufacturing, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems play a crucial role in streamlining operations. Yet, even with technological advancements, bottlenecks can arise, impeding the flow of production. Here, we explore some prevalent hurdles faced in the ERP manufacturing process:
Production Delays
Bottlenecks often surface when certain production stages falter, causing a ripple effect across operations. If a machine demands frequent maintenance or functions at a slower rate compared to others, it can stall the entire production line. Such delays not only affect schedules but also escalate operational costs.
Inefficient Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is pivotal in avoiding excess inventory or out-of-stock scenarios. Overloading inventory unnecessarily ties up capital, while a shortage can grind production to a halt. Both extremes disrupt the seamless flow of materials, delay production timelines, and impact revenue.
Absence of Real-Time Data
Having access to real-time data is critical for informed decision-making. When data is inaccurate or outdated, it hinders the ability to promptly identify and resolve issues within the ERP system. This lack of visibility leads to inefficiencies, as it’s difficult to determine where and when production obstacles arise.
Inadequate Communication Channels
Communication breakdowns between teams or departments can significantly slow down production. When vital information isn’t shared promptly, it generates misunderstandings and errors. These lapses can cause unnecessary delays, impacting the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
These bottlenecks highlight the need for robust ERP solutions that enhance transparency, improve coordination, and streamline operations to ensure a fluid and efficient manufacturing process.
How to apply Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Kaizen to ERP Processes?
Optimizing ERP processes is essential for enhancing efficiency and quality in manufacturing. Three methodologies—Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Kaizen—offer robust frameworks for driving continuous improvement and can be effectively applied to ERP systems. Incorporating value stream mapping into these methodologies can further streamline ERP processes.
Lean Manufacturing: Streamlining and Efficiency
Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste while enhancing productivity. When applied to ERP processes, this approach can streamline production workflows and reduce unnecessary activities. For example:
- Streamlined Workflows: Simplify production processes by removing redundant steps, ensuring that ERP systems facilitate faster and more efficient operations.
- Inventory Optimization: Reduce excess inventory by utilizing ERP tools to maintain just-in-time stock levels, minimizing costs.
- Waste Elimination: Identify and eliminate non-value-added tasks in ERP functions, creating a leaner and more agile operation.
Six Sigma: Quality and Precision
Six Sigma methodologies aim to minimize defects and variability. Integrating Six Sigma into ERP processes involves using data-driven strategies to enhance overall system quality and reliability:
- Data Analysis: Employ statistical tools within the ERP to pinpoint and resolve inefficiencies, thus improving the accuracy of operations.
- Process Standardization: Establish uniform procedures and metrics within the ERP to maintain high-quality outputs and minimize errors.
- Customer Satisfaction: Improve product and service quality, directly benefiting customer experience and satisfaction.
Kaizen: Continuous Improvement and Employee Engagement
Kaizen focuses on ongoing improvement and involves every employee in the enhancement of processes. Incorporating Kaizen in ERP systems encourages a continuous evolution of processes:
- Collaborative Meetings: Host regular sessions where teams review ERP workflows, identifying opportunities for incremental improvements.
- Culture of Innovation: Foster an environment where every team member contributes ideas to enhance ERP functionality and service.
- Adaptation: Encourage agility within the ERP system to quickly adapt to industry changes and new challenges.
By applying these methodologies, ERP systems become more efficient, precise, and adaptive, leading to improved overall performance and competitive advantage.
Value stream mapping (VSM) and workflow analysis are essential techniques for uncovering bottlenecks in manufacturing processes. Here’s how each contributes to streamlining production:
Do you know what is Value Stream Mapping (VSM)?
VSM is an invaluable tool that provides a visual representation of your entire manufacturing process. This visualization covers everything from the intake of raw materials to the delivery of finished products. By mapping each stage, VSM helps identify delays and inefficiencies that may not be apparent at first glance. This comprehensive view enables you to spot which steps are causing slowdowns, allowing you to target and optimize these critical areas effectively.
Workflow Analysis
Workflow analysis delves deeper into examining each step of your production process. It’s all about dissecting the workflow to uncover hidden inefficiencies. By analyzing these processes meticulously, you can identify specific points where bottlenecks occur. Once these are pinpointed, you can investigate their root causes, which might include equipment malfunctions, staffing issues, or procedural errors.
Through both VSM and workflow analysis, companies can gain a clearer perspective on their operations. These methodologies do more than surface-level diagnostics—they uncover the underlying issues that, when addressed, can significantly enhance efficiency and productivity in the manufacturing process.
Your successful ERP systems strategy with InvestGlass
In conclusion, digital transformation through ERP systems is more than just business management software; it is a strategic investment for any business aiming for growth and efficiency. By integrating and automating key business functions, an ERP solution can transform the entire business, aiding in achieving better business performance and setting the foundation for a bright, sustainable future.
The decision to transition to a new system, especially a new ERP system, is significant. But with the right ERP vendor and a careful implementation process, businesses can navigate this change successfully and set themselves up for long-term success.
Remember, as with any enterprise system, the ERP life cycle is ongoing; regular updates and improvements are key to ensuring that the ERP solution continues to meet the needs of the evolving business landscape.